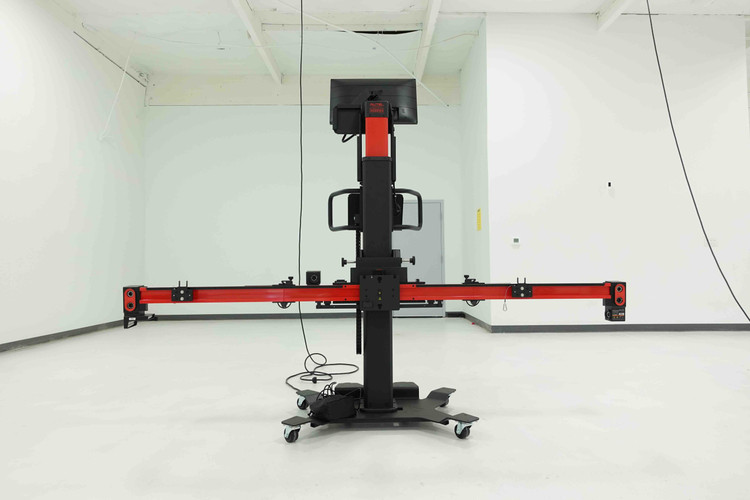
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) have become integral components in modern vehicles, enhancing safety and driving experiences. Calibration of these systems is a crucial step to ensure their accuracy and reliability. Two common methods employed in ADAS calibration are stationary and mobile frames, each with its own set of advantages and limitations. In this blog post, we will delve into the differences between stationary and mobile ADAS calibration frames to help you understand which approach might be the most suitable for your needs.
- Stationary ADAS Calibration Frames:
- Fixed Setup: Stationary calibration frames are installed in a fixed location, typically within a dedicated facility or workshop. This fixed setup allows for a controlled environment, minimizing external variables that could affect calibration accuracy.
- Precision and Accuracy: The stationary setup provides a stable and controlled environment, contributing to precise and accurate calibration. Factors like wind, temperature, and other external elements are minimized, ensuring consistency in calibration results.
- Time-Consuming: One of the drawbacks of stationary frames is that they can be time-consuming. Vehicles need to be brought to and from the calibration facility.
- Limited Accessibility: Accessibility is a potential limitation, as not all vehicles can be driven to a calibration facility. In some cases, particularly for heavy-duty vehicles or agricultural machinery, transporting the vehicle to the calibration site might be impractical.
- Mobile ADAS Calibration Frames:
- Flexibility and Convenience: Mobile calibration frames offer greater flexibility, as they can be transported to a location of choice. This is particularly advantageous for fleet operators, mobile service providers, or situations where bringing the vehicle to a fixed facility is challenging.
- On-Site Calibration: With mobile frames, calibration can be performed on-site, eliminating the need to transport the vehicle. This not only saves time but also increases the accessibility of calibration services.
- Environmental Variables: On the flip side, mobile calibration frames may be used in environments where the floor is not perfectly level, or the lighting conditions are poor. Achieving the same level of controlled conditions as a stationary setup can be challenging.
Conclusion:
Choosing between stationary and mobile ADAS calibration frames depends on various factors, including the nature of the vehicle fleet, the frequency of calibration required, and the convenience of on-site calibration. Stationary frames provide a controlled environment, ensuring precision but might be less accessible. On the other hand, mobile frames offer flexibility and convenience, making them suitable for various scenarios but with potential challenges in maintaining controlled conditions.
In the ever-evolving landscape of automotive technology, both stationary and mobile ADAS calibration frames play crucial roles in keeping our roads safe. The decision between the two depends on finding the right balance between precision, accessibility, and convenience for your specific needs.
If you liked this content, please subscribe to our newsletter for more great posts.